Understanding Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, And Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL) have become transformative forces in today's technological landscape. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct yet interconnected concepts. From powering voice assistants to revolutionizing industries, AI, ML, and DL are reshaping how we live, work, and interact with the world. Understanding these technologies is essential for anyone looking to stay informed about the future of innovation.
As we delve deeper into this guide, we will explore the definitions, differences, and applications of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply curious about these technologies, this article aims to provide a clear and comprehensive overview. By the end of this guide, you'll have a solid understanding of how AI, ML, and DL work and their implications for various sectors.
In recent years, advancements in AI have accelerated, driven by the availability of massive datasets, powerful computing resources, and innovative algorithms. This has led to breakthroughs in fields such as healthcare, finance, and transportation. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Ethical considerations and challenges surrounding AI adoption must also be addressed to ensure these technologies benefit humanity as a whole.
Read also:Erika Buenfil Net Worth 2023 A Look Inside
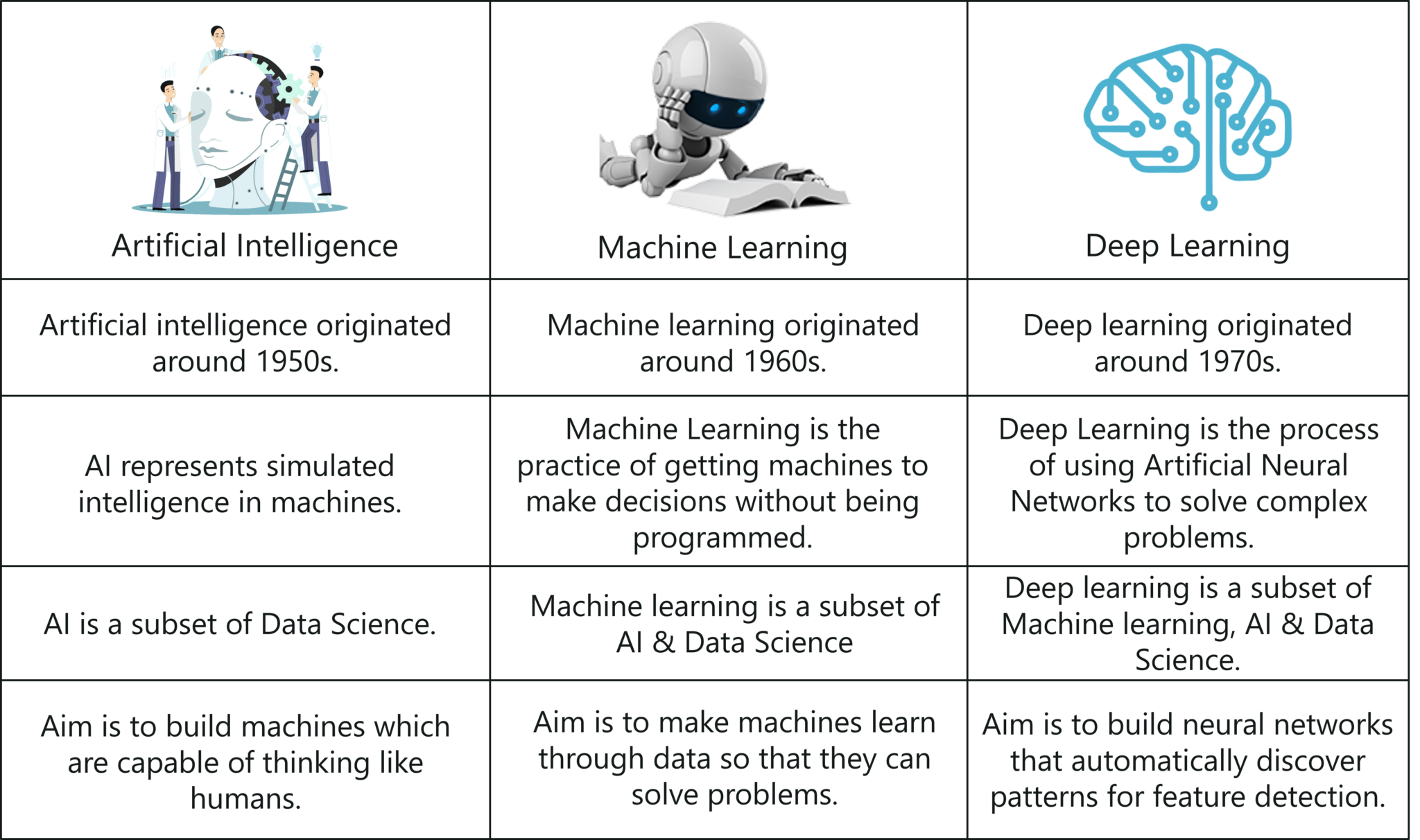
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence by machines. It encompasses a wide range of capabilities, including problem-solving, decision-making, and language understanding. AI systems are designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing patterns, learning from experience, and adapting to new situations.
There are two main types of AI: narrow AI and general AI. Narrow AI, also known as weak AI, is designed to perform specific tasks, such as facial recognition or language translation. General AI, on the other hand, refers to systems that possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a wide range of tasks, similar to human cognition. While narrow AI is already widely used, general AI remains a theoretical concept and is yet to be fully realized.
Key Characteristics of AI
- Automation: AI enables machines to perform repetitive tasks without human intervention.
- Learning: AI systems can improve their performance over time through experience.
- Reasoning: AI can analyze data and make decisions based on logical reasoning.
- Perception: AI can interpret sensory data, such as images and sounds, to understand the environment.
Machine Learning Explained
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on enabling machines to learn from data. Instead of being explicitly programmed, ML algorithms use statistical techniques to identify patterns and make predictions or decisions. This approach allows systems to improve their performance over time without human intervention.
There are three main types of machine learning: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data, where the input and output are known. Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, deals with unlabeled data and aims to uncover hidden patterns. Reinforcement learning involves training a model to make decisions by rewarding desired behaviors and penalizing undesired ones.
Applications of Machine Learning
- Recommendation Systems: Platforms like Netflix and Amazon use ML to suggest products and content based on user preferences.
- Fraud Detection: Banks and financial institutions use ML algorithms to detect unusual transactions and prevent fraud.
- Image Recognition: ML powers applications like facial recognition and object detection in images.
Deep Learning Unveiled
Deep learning is a specialized form of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to process information. These networks are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, consisting of layers of interconnected nodes, or "neurons." Deep learning models can automatically learn hierarchical representations of data, making them particularly effective for complex tasks.
One of the key advantages of deep learning is its ability to handle large datasets and extract meaningful insights. This has led to breakthroughs in areas such as natural language processing, computer vision, and autonomous systems. However, deep learning models require significant computational resources and large amounts of labeled data for training.
Read also:Is Jacob Elordi In A Relationship Everything You Need To Know
Key Components of Deep Learning
- Neural Networks: The foundation of deep learning, neural networks consist of input, hidden, and output layers.
- Backpropagation: A technique used to train neural networks by adjusting weights based on errors.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Specialized networks used for image and video analysis.
Applications of AI, ML, and DL
The applications of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning are vast and varied. These technologies are being used to solve real-world problems and drive innovation across industries. From healthcare to finance, AI, ML, and DL are transforming the way businesses operate and how individuals interact with technology.
For example, in the field of healthcare, AI-powered systems are being used to diagnose diseases, predict patient outcomes, and personalize treatment plans. In finance, machine learning algorithms are used to detect fraud, assess credit risk, and optimize investment strategies. Meanwhile, deep learning is enabling advancements in autonomous vehicles, robotics, and natural language processing.
Examples of AI Applications
- Virtual Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use AI to understand and respond to user queries.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on AI and deep learning to navigate and make decisions.
- Smart Home Devices: AI-powered devices like thermostats and security systems enhance convenience and safety.
AI in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by improving patient care, streamlining operations, and enabling breakthroughs in medical research. AI-powered tools are being used to analyze medical images, predict disease outbreaks, and assist in surgical procedures.
One notable example is the use of AI in radiology. Deep learning models can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, with remarkable accuracy, helping doctors detect abnormalities and make informed decisions. Additionally, AI-driven predictive analytics are being used to identify patients at risk of developing chronic conditions, allowing for early intervention and personalized treatment plans.
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
- Improved Diagnostics: AI enhances the accuracy and speed of disease detection.
- Personalized Medicine: AI enables tailored treatment plans based on individual patient data.
- Operational Efficiency: AI automates administrative tasks, reducing costs and improving workflow.
AI in Finance
The financial industry has embraced artificial intelligence to enhance decision-making, improve customer experiences, and mitigate risks. AI-powered tools are being used for fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading, and customer service automation.
For instance, machine learning algorithms can analyze transaction data to identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activity. Similarly, AI-driven credit scoring models assess a borrower's risk profile by analyzing alternative data sources, such as social media activity and transaction history. These innovations not only improve accuracy but also expand access to financial services for underserved populations.
AI-Driven Innovations in Finance
- Robo-Advisors: AI-powered platforms provide personalized investment advice at a fraction of the cost.
- Risk Management: AI models predict market trends and assess portfolio risks.
- Chatbots: AI-driven virtual assistants handle customer inquiries and resolve issues efficiently.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning offer immense potential, they also pose significant challenges and ethical considerations. Issues such as bias, transparency, privacy, and accountability must be addressed to ensure these technologies are used responsibly and equitably.
One major concern is algorithmic bias, where AI systems perpetuate or amplify existing societal biases. This can lead to unfair outcomes, particularly in areas such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement. Additionally, the lack of transparency in AI decision-making processes raises questions about accountability and trust.
Addressing Ethical Challenges
- Data Privacy: Ensure user data is collected and used in compliance with privacy regulations.
- Bias Mitigation: Implement techniques to detect and reduce bias in AI models.
- Transparency: Provide clear explanations of how AI systems make decisions.
Future of AI, ML, and DL
The future of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning is promising, with continued advancements expected in the coming years. These technologies will play a pivotal role in shaping industries, driving innovation, and addressing global challenges.
Emerging trends such as explainable AI, federated learning, and quantum computing are set to further enhance the capabilities of AI systems. Additionally, the integration of AI with other technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain, will unlock new possibilities and applications.
Predictions for the Future
- AI-Powered Automation: Increased adoption of AI in manufacturing, logistics, and service industries.
- Human-AI Collaboration: Enhanced partnerships between humans and AI systems to solve complex problems.
- AI for Sustainability: AI applications to address environmental challenges and promote sustainable development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning are transforming the world as we know it. These technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to improve efficiency, enhance decision-making, and drive innovation across industries. However, their adoption must be guided by ethical principles to ensure they benefit society as a whole.
We encourage you to explore further resources and stay informed about the latest developments in AI, ML, and DL. If you found this guide helpful, please share it with others and leave a comment with your thoughts. For more insights, check out our other articles on emerging technologies and their impact on the future.
Schwartzfarb Sell More Faster Download: Boost Your Sales With Proven Strategies
Vietnam Holidays 2018: A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The Beauty Of Southeast Asia
Tax Arbitrage Through Cross-Border: A Comprehensive Guide To Maximizing Financial Opportunities
Machine Learning Vs Artificial Intelligence Vs Deep Learning Artificial

Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning